Java Overview
Java is an open-source, class-based, high-level, object-oriented programming language. Java is platform independent as the java programs are compiled into byte code that are platform independent.
History:
Java programming language was created by James Gosling in 1995. The original idea was to design a language for the television industry. Gosling worked along with his team also called the Green Team and the project they worked on was called Greentalk. This project was later named as OAK. The name OAK has its roots to the oak tree that stood outside Gosling’s office. This name had to be dropped later as it was already a trademark by Oak Technologies.
So how was the name Java suggested?
Since the language could no longer be named OAK, Gosling and his team had to come up with new name. The team considered various names like DNA, RUBY, JAVA, jolt, dynamic, revolutionary, SILK.
But the name had to unique and quite easy to say. The name JAVA occurred in gosling’s mind while having a cup of coffee at his office.
Types of Java applications:
A. Web Application:
Web applications are the applications that run on web browser using servlet, JSP, struts technologies. These technologies create java web applications and deploy them on server.
B. Mobile Application:
These are mobile applications created using java.
C. Standalone Application:
Standalone applications are executed by themselves without the need of other programs and files. Example of such an application is antivirus.
D. Enterprise Application:
Some applications are designed for corporate organizations with the intent to control major process in real time. Such applications are called enterprise applications.
Features
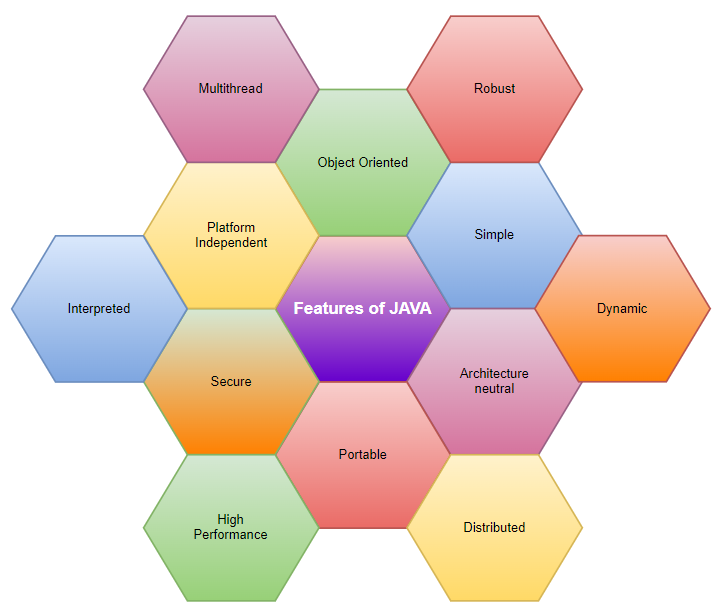
- Object Oriented: In object oriented programming everything is an object rather that function and logic.
- Simple: Java is simple to understand, easy to learn and implement.
- Secured: It is possible to design secured software systems using Java.
- Platform Independent: Java is write once and run anywhere language, meaning once the code is written, it can be executed on any software and hardware systems.
- Portable: Java is not necessarily fixated to a single hardware machine. Once created, java code can be used on any platform.
- Architecture Neutral: Java is architecture neutral meaning the size of primitive type is fixed and does not vary depending upon the type of architecture.
- Robust: Java emphasizes a lot on error handling, type checking, memory management, etc. This makes it a robust language.
- Interpreted: Java converts high-level program statement into Assembly Level Language, thus making it interpreted.
- Distributed: Java lets us create distributed applications that can run on multiple computers simultaneously.
- Dynamic: Java is designed to adapt to ever evolving systems thus making it dynamic.
- Multi-thread: multi-threading is an important feature provided by java for creating web applications.
- High-performance: Java uses Just-In-Time compiler thus giving us a high performance.
Installation & Setup
Step 1:
Before starting the installation processes, it is advisable to check if your PC already has Java installed. To do this, open the command prompt and type the following:
Output:
Step 2:
If your system does not have Java installed, download it from the official website: https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/downloads/
Step 3:
Run the downloaded file to install Java on your machine.
Step 4:
- Right click on This PC (My Computer).
- Click on properties.
- Go to Advanced System Settings.
- Under this click on Environment Variables.
- Inside System Variables, select Path and click on Edit.
- Give the path of directory where Java is installed followed by a \bin.
- Repeat step 1 to check if Java has been set up and running on your machine.
Java programs can be written in normal text editor like a notepad or more complicated editors(IDE’s) like Netbeans, Eclipse or Visual Studio Code.
For the sake of this tutorial, we will be using Visual Studio Code.
JVM, JRE, JDK

A. Java Virtual Machine (JVM):
The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is a virtual machine that provides a runtime environment to execute java bytecode.
The java program is converted into java bytecode which is then translated by the JVM into machine code which can be then understood by the CPU to get the output.
B. Java Runtime Environment (JRE):
The Java Runtime Environment (JRE) provides java libraries, the JVM and other files and documents that are needed to run java applications.
C. Java Development Kit (JDK):
The Java Development Kit (JDK) is a superset of JRE and is used to create java applications. There are three JDK provided by Oracle; Java Enterprise Edition (Java EE), Java Standard Edition (Java SE), and Java Mobile Edition (Java ME).



0 Comments