React Lists
In React we render lists with loop
map()
An example of map:
Output:
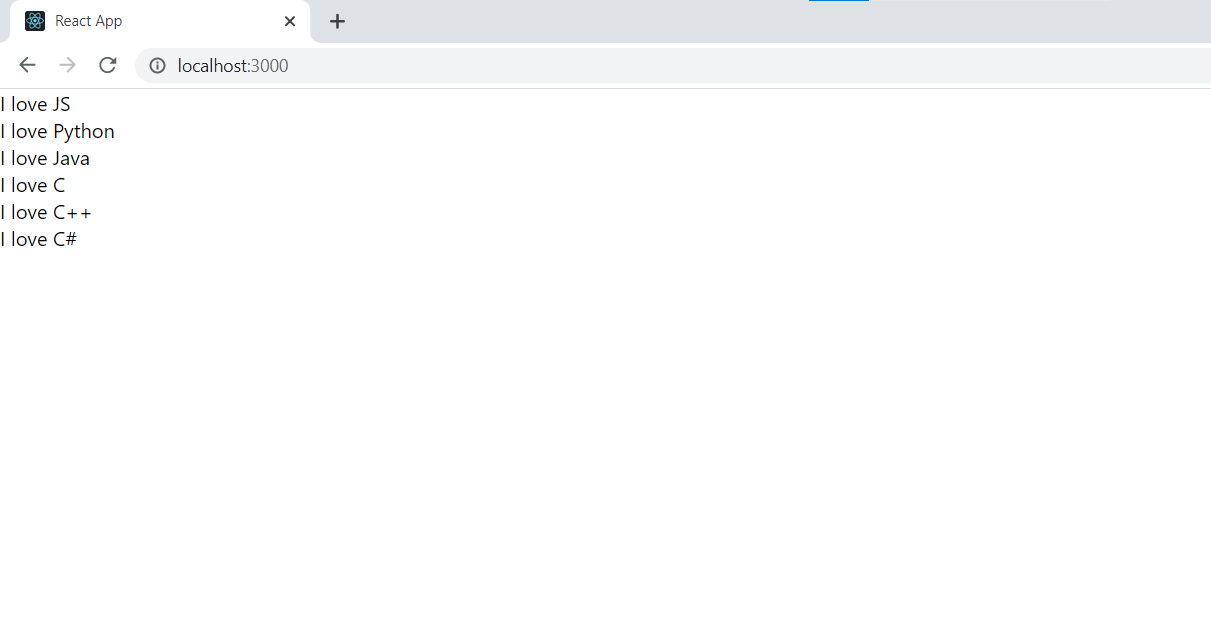
Keys
With keys React keep record of elements. This ensures that if an item is updated or removed, only that item will be re-rendered instead of the entire list. Example:
Output:
An example of map:
Output:

React Forms
React Forms are mostly like normal HTML forms, except we use state in this to handle inputs.
Handling Forms
In React all the data is handled by component and stored in component state. We can change state with event handlers in the onChange attribute, like this:
Submitting Form
We can submit form with onSubmit attribute for the <form>
Multiple Inputs
We don't have to make multiple states for multiple inputs, we can save all values in one, like this:
Here in handleChange we used Spread Operators. We are basically saying keep whole data as it was, just change this name's value. Then it is saved as an object so we are getting that by data.email and data.name.
React Router
React router is used for page routing as React App doesn't include it as default.
Add React Router
To install React router, run this in your terminal:
Creating Multiple Routes
To do this first we need to create multiple files and to keep code clean, we will make a folder and make all the pages there, hence we will create a folder named pages in src.
Folder Structure:
src/pages/:
Home.jsBlogs.jsContact.jsNopage.js
Usage
Now we will make routes in src/index.js, like this:
Home.js
Make all the Navigation links using <Link> tag, like this:
Blogs.js
Contact.js
NoPage.js
This is made for any route that doesn't exist. To show 404 error there!



0 Comments